Confined Space Entry (CSE) and Rescue
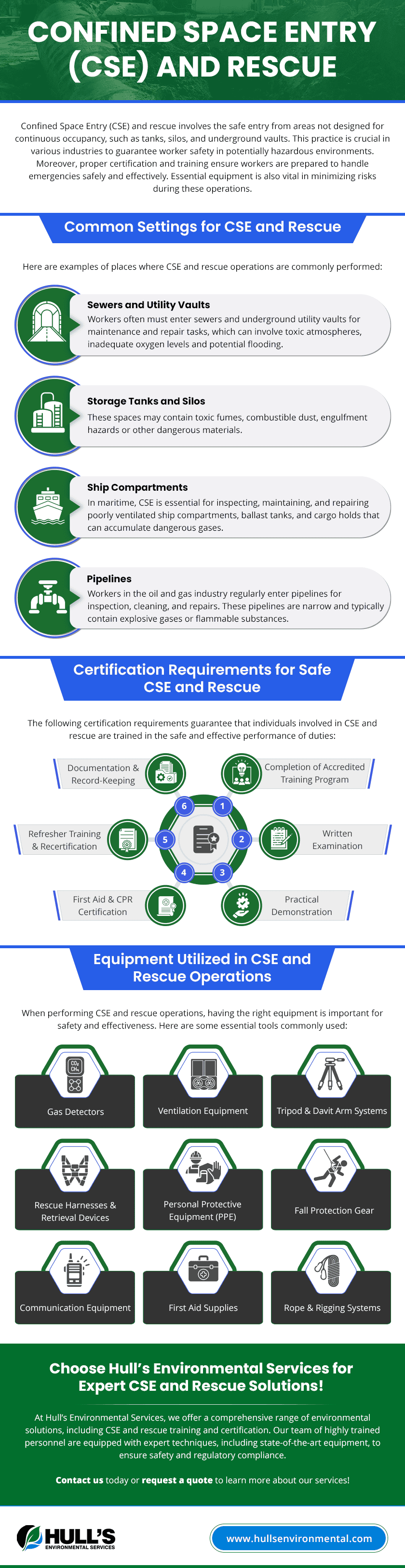
Comments Off on Confined Space Entry (CSE) and RescueConfined Space Entry (CSE) and rescue involves the safe entry from areas not designed for continuous occupancy, such as tanks, silos, and underground vaults. This practice is crucial in various industries to guarantee worker safety in potentially hazardous environments. Moreover, proper certification and training ensure workers are prepared to handle emergencies safely and effectively. Essential equipment is also vital in minimizing risks during these operations.
This article explores the essential training and certification needed for personnel in CSE and rescue operations, along with the equipment required for guaranteeing safe entries and meeting all the OSHA requirements in 29 CFR 1910.146 (CSE standard). OSHA has clearly stated that using only 911 for CSE rescue does not meet the standard and is a violation of the rule.
Common Settings for CSE and Rescue
Here are examples of places where CSE and rescue operations are commonly performed:
- Sewers and utility vaults: Workers often must enter sewers and underground utility vaults for maintenance and repair tasks, which can involve toxic atmospheres, inadequate oxygen levels and potential flooding.
- Storage tanks and silos: These spaces may contain toxic fumes, combustible dust, engulfment hazards or other dangerous materials.
- Ship compartments: In maritime, CSE is essential for inspecting, maintaining, and repairing poorly ventilated ship compartments, ballast tanks, and cargo holds that can accumulate dangerous gases.
- Pipelines: Workers in the oil and gas industry regularly enter pipelines for inspection, cleaning, and repairs. These pipelines are narrow and typically contain explosive gases or flammable substances.
Certification Requirements for Safe CSE and Rescue
The following certification requirements guarantee that individuals involved in CSE and rescue are trained in the safe and effective performance of duties:
1. Completion of Accredited Training Program
Candidates must complete a training program from an accredited institution recognized by OSHA, ANSI, or NFPA. These programs cover essential topics such as regulations, hazard recognition, equipment use, air monitoring, and rescue techniques to ensure comprehensive understanding and skill development.
2. Written Examination
Trainees must undergo a written exam to evaluate the theoretical knowledge gained from the training. The exam aims to meet the certifying authority’s minimum threshold, demonstrating proficiency in confined space entry and rescue principles.
3. Practical Demonstration
Practical skills are tested in a controlled environment where candidates must demonstrate proficiency in handling equipment, understanding the dangers associated with a hazardous atmosphere, executing entry and exit procedures, and performing rescue operations. This hands-on assessment is crucial for ensuring readiness for real-world scenarios.
4. First Aid and CPR Certification
Candidates are required to hold current certifications in first aid and CPR from recognized organizations like the American Red Cross or the American Heart Association. This requirement makes sure that they can provide immediate medical assistance during emergencies.
5. Refresher Training and Recertification
Certification often necessitates periodic refresher training, usually annually, to stay updated with the latest regulations and techniques. Continuous education is essential to maintaining certification status and competency.
6. Documentation and Record-Keeping
Accurate records of all training sessions, certifications, and refresher courses are necessary for compliance and verification. All OSHA required confined space entry permits will be completed, reviewed, and approved before any operations are started at a site. Additionally, records of entry permits and any incidents or near-misses must be meticulously documented as part of the certification requirements.
Equipment Utilized in CSE and Rescue Operations
When performing CSE and rescue operations, having the right equipment is important for safety and effectiveness. Here are some essential tools commonly used:
- Gas detectors monitor the atmosphere for toxic gases or vapors, oxygen, carbon monoxide, flammability, and hydrogen sulfide levels.
- Ventilation equipment is essential for purging hazardous atmospheres, with intrinsically safe electric blowers preferred in flammable environments.
- Tripod and davit arm systems provide a stable platform for non-entry rescues, especially in vertical entry scenarios like tanks and silos.
- Rescue harnesses and retrieval devices require comfort, easy adjustment, and security features to ensure safe entry, exit, and rescue.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) includes hard hats, safety goggles, full-face respirators, protective clothing, and gloves, protecting from physical hazards and hazardous atmospheres.
- Fall protection gear prevents falls and guarantees safety in unstable environments, comprising harnesses, lifelines, lanyards, and anchor connectors.
- Communication equipment ensures communication between rescuers and outside personnel, which is vital in coordination and safety during rescue operations.
- First aid supplies provide immediate medical attention to injured individuals, particularly in confined spaces.
- Rope and rigging systems lower and lift personnel and equipment safely, and they need to be robust and suitable for the confined space environment.
Choose Hull’s Environmental Services for Expert CSE and Rescue Solutions!
At Hull’s Environmental Services, we offer a comprehensive range of environmental solutions, including CSE and rescue training and certification. Our team of highly trained personnel are equipped with expert techniques, including state-of-the-art equipment, to ensure safety and regulatory compliance.
Contact us today or request a quote to learn more about our services!
Waste Disposal
Comments Off on Waste DisposalWaste disposal involves the safe, organized, and responsible handling and elimination of waste materials generated by human activities. Understanding various disposal methods is crucial under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). These methods encompass traditional options, such as landfills and incineration, and innovative alternatives, like recycling and bioremediation. Each method presents its advantages and challenges.
This article discusses methods for disposing of hazardous and non-hazardous waste, emphasizing the importance of employing appropriate approaches to safeguard public health and the environment.
Landfills
Land disposal involves burying or dumping waste in designated areas known as landfills. These sites are carefully engineered with liners, leachate collection systems, and monitoring to prevent contaminating the surroundings. While effective for large volumes of waste, landfills require adequate space and can pose long-term environmental risks if not properly managed.
Incineration
Incineration involves burning waste at high temperatures to reduce its volume and eliminate hazardous components, effectively reducing landfill waste and generating energy. However, incineration emits pollutants, necessitating stringent pollution control measures to mitigate air pollution and ensure the safe handling of residues.
Recycling
Recycling involves collecting, sorting, and reprocessing waste materials to create new products. While more commonly associated with non-hazardous waste, certain hazardous materials can also be recycled if they can be safely treated and reused. Recycling conserves resources, reduces landfill waste, and can be economically beneficial.
Treatment
Treatment methods involve using chemical, physical, or biological processes to neutralize or stabilize hazardous waste, making it less harmful or easier to handle. Chemical precipitation, oxidation, and bioremediation are common treatment techniques. These processes can reduce the toxicity of waste but may generate secondary waste streams and require specialized facilities.
Secure Land Disposal Facilities
Secure land disposal facilities are engineered to isolate highly toxic or persistent hazardous waste from the environment for long periods. These facilities, such as deep geological repositories, employ multiple barriers and containment measures to prevent contamination of soil and water resources. They are designed for waste with long-term hazards or unknown future risks.
Waste-to-Energy (WTE) Facilities
WTE facilities use waste as a fuel to generate energy through processes including combustion or gasification. While primarily used for municipal solid waste, some facilities can handle certain types of hazardous waste. WTE also reduces the volume of waste going to landfills and generates renewable energy, but it requires careful management of emissions and ash residues.
Hazardous Waste Landfills
Specialized hazardous waste landfills are designed specifically for the disposal of hazardous waste. These facilities have stringent waste acceptance, handling, and containment requirements to minimize environmental risks and protect public health. They are equipped with liners, leachate collection systems, and monitoring to prevent soil and groundwater contamination.
Bioremediation
Bioremediation utilizes microorganisms or plants to degrade or neutralize hazardous substances in soil or water. It offers a natural and sustainable approach to waste remediation, but its effectiveness depends on site conditions, contaminant type, and microbial activity. Bioremediation can be cost-effective for certain types of contamination.
Encapsulation
Encapsulation involves immobilizing hazardous waste in materials, such as concrete or epoxy. This method prevents contaminants from leaching into the environment and is often used for waste that cannot be easily disposed of using other methods. However, encapsulation may not address underlying contamination sources and requires careful design and construction.

Choose Hull’s Environmental Services for Expert Waste Disposal Solutions!
At Hull’s Environmental Services, we specialize in waste disposal and transportation, serving as your reliable environmental partner for comprehensive waste management solutions. Our commitment to delivering high-quality service guarantees that every task is completed accurately on the initial attempt, saving you valuable time and resources.
Contact us today or request a quote to get started!